-40%
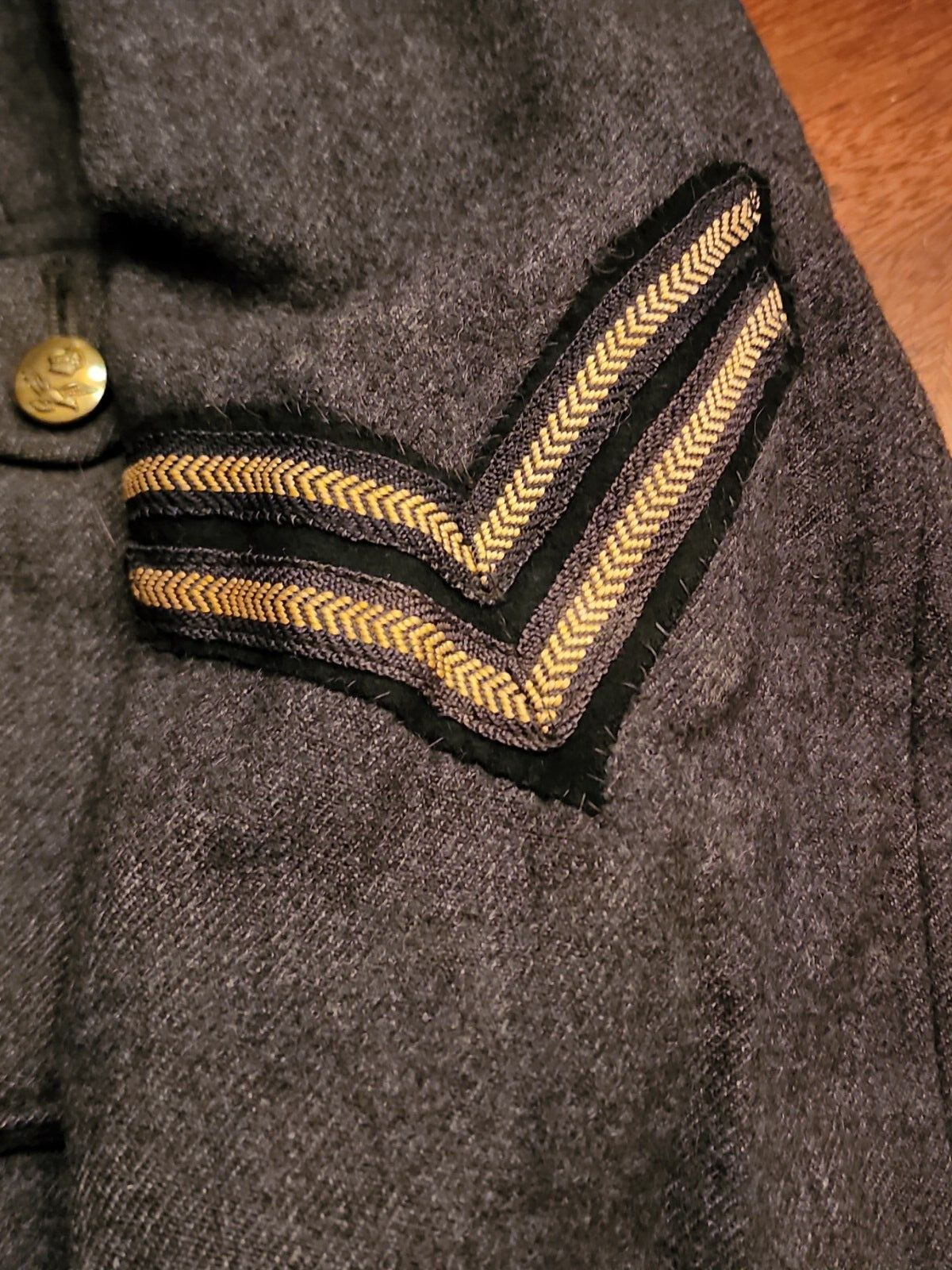
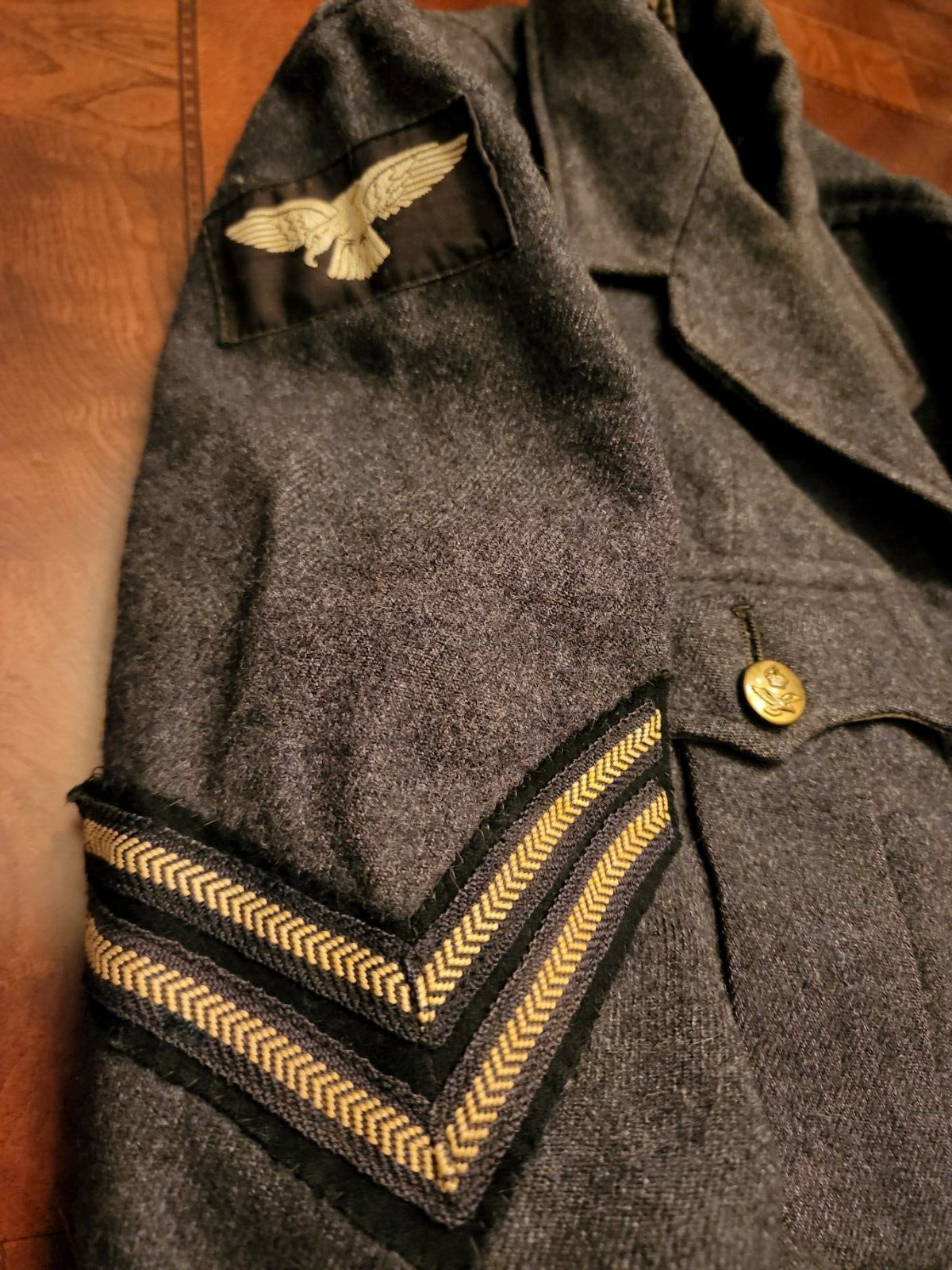
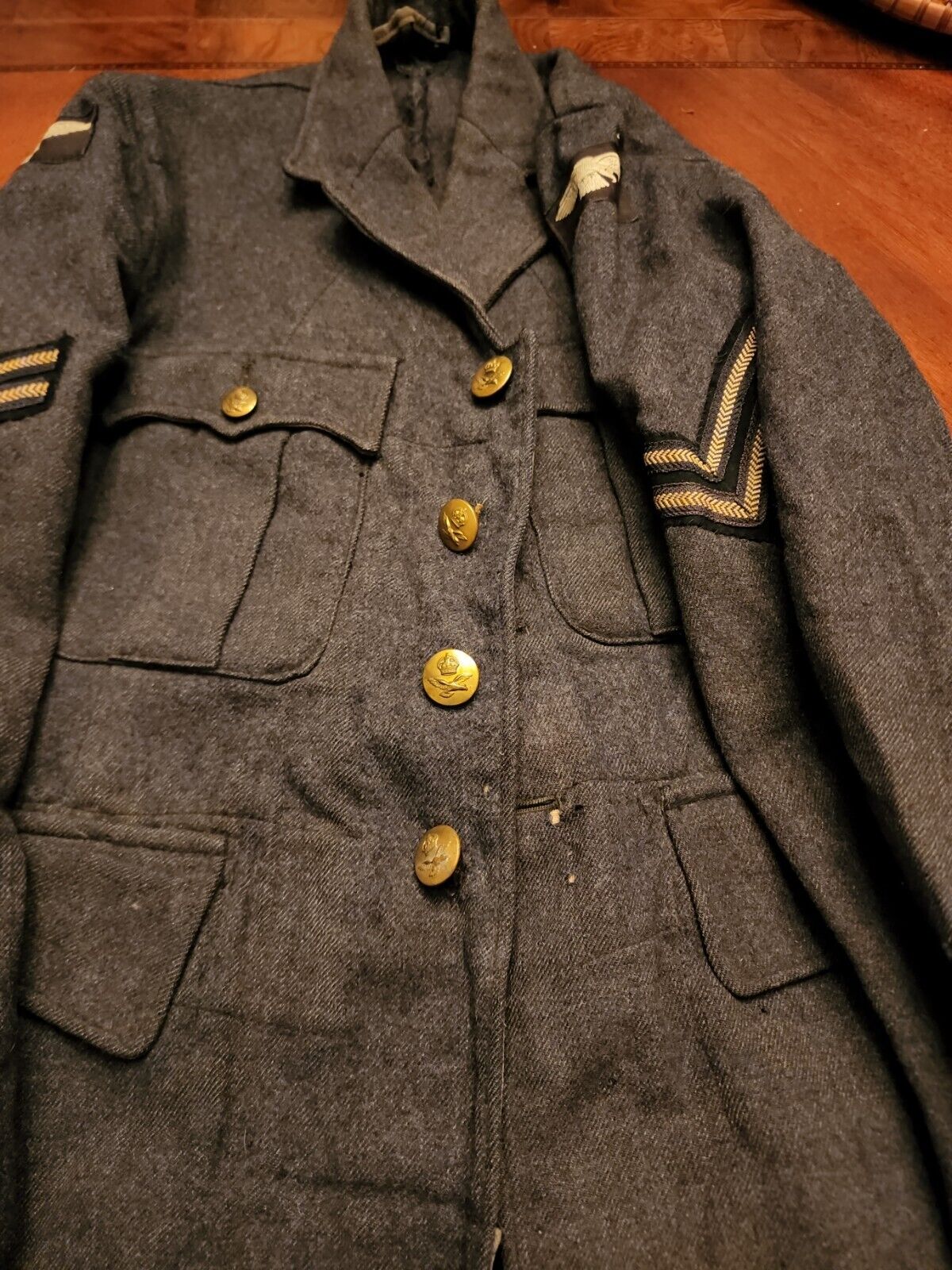
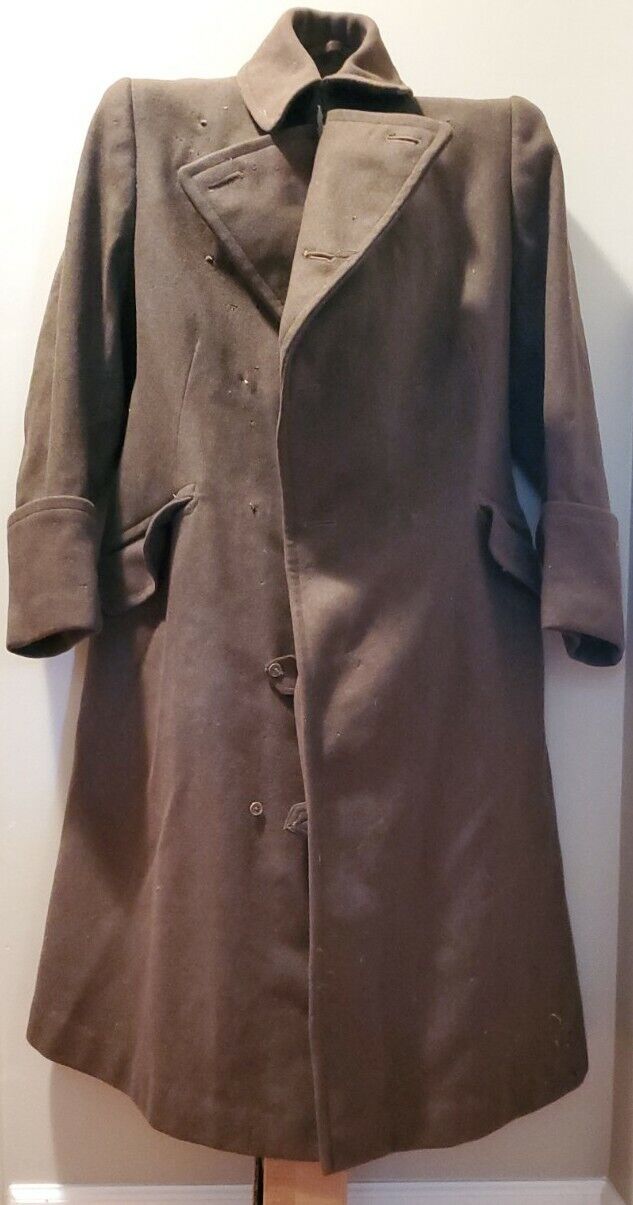
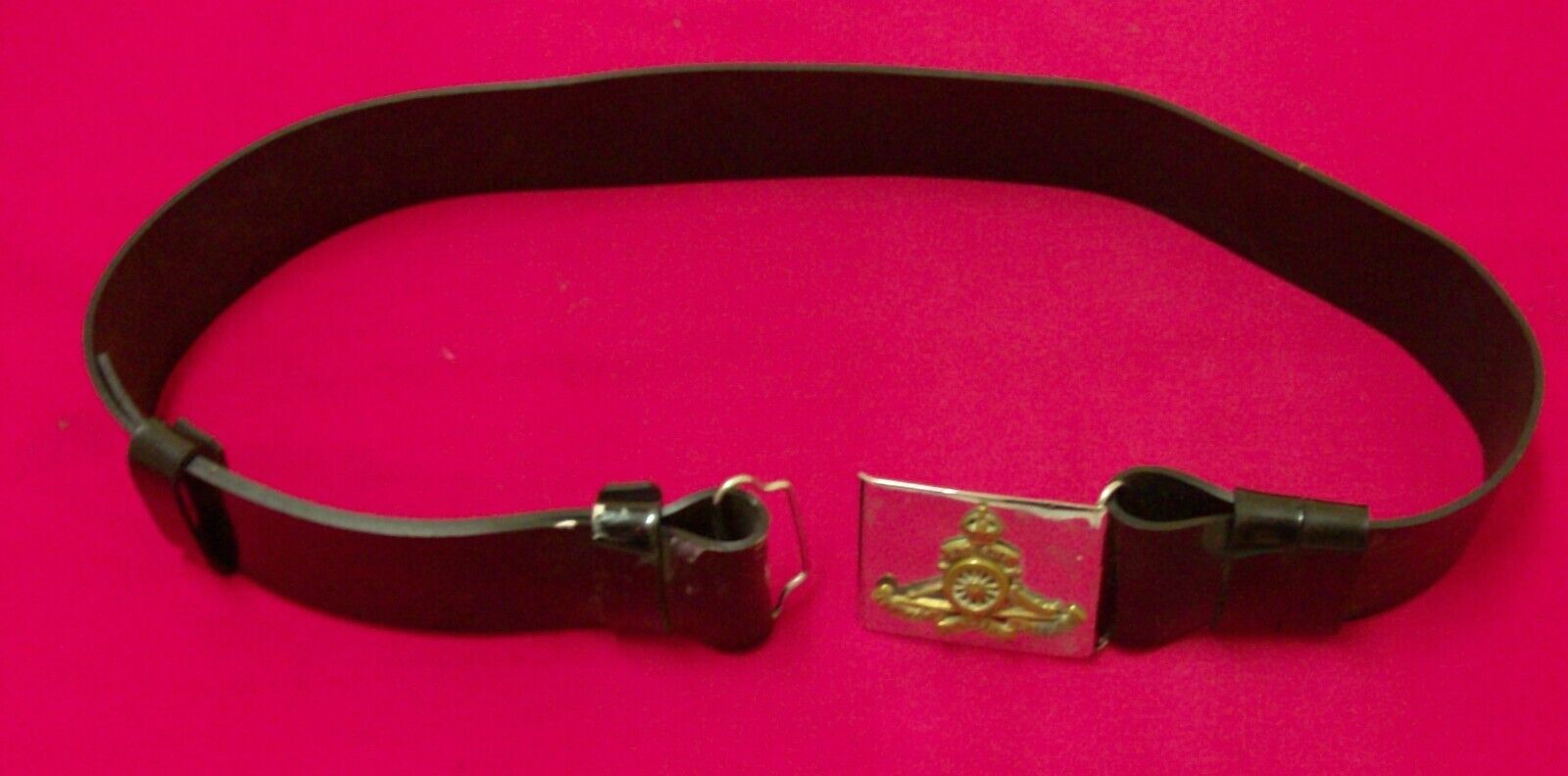
WW2 RAF SERGENT JACKET VERY RARE SEE STORE WW2 MEDALS UNIFOMS DEALS GALORE !!!!
$ 263.99
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
PLEASE FOLLOW OUR E BAY STORESEE ALL PICS
SALE
SEE OUR STORE
PLEASE READ WHOLE ADD
size # 6
Royal Air Force
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
"RAF" redirects here. For other uses, see
RAF (disambiguation)
and
Royal Air Force (disambiguation)
.
Royal Air Force
Badge of the Royal Air Force
Founded
1 April 1918
; 104 years ago
Country
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
(1918–1922)
United Kingdom
(1922–present)
Type
Air force
Role
Aerial warfare
Size
33,200 active personnel
[1]
1,940
Royal Auxiliary Air Force
3,300 reserve personnel
[1]
[note 1]
Part of
British Armed Forces
Air Staff Offices
Whitehall
,
London
Motto(s)
"
Per Ardua ad Astra
"
(
Latin
)
(Through Adversity to the Stars)
March
Quick:
Royal Air Force March Past
Slow: Saeculum
[2]
Website
www
.raf
.mod
.uk
Commanders
Commander-in-Chief
Elizabeth II
Chief of the Air Staff
Air Chief Marshal
Sir Mike Wigston
Warrant Officer of the Royal Air Force
Warrant Officer
Jake Alpert
Notable
commanders
Lord Trenchard
Lord Portal
Insignia
Logo
Roundel
Fin flash
Ensign
Aircraft flown
Attack
General Atomics MQ-9A Reaper
Fighter
Eurofighter Typhoon FGR4
Lockheed Martin F-35B Lightning
Multirole helicopter
Bell Griffin HAR2
Boeing Chinook HC4/5/6/6A
Leonardo AW109SP GrandNew
Westland Puma HC2
Trainer helicopter
Airbus Helicopters Juno HT1
Airbus Helicopters Jupiter HT1
Reconnaissance
Boeing P-8 Poseidon MRA1
Boeing RC-135W Rivet Joint
General Atomics MQ-9A Reaper
Hawker Beechcraft Shadow R1/R1A
Trainer
BAE Hawk T1/T2
Beechcraft Texan T1
Embraer Phenom T1
Eurofighter Typhoon T3
Grob Viking T1
Grob Prefect T1
Grob Tutor T1
Transport
Airbus Voyager KC2/KC3
Airbus A400M Atlas C1
Boeing C-17 Globemaster III
Lockheed Martin Hercules C4/C5
Tanker
Airbus Voyager KC2/KC3
The
Royal Air Force
(
RAF
) is the
United Kingdom
's
air
and
space force
.
[3]
It was formed towards the end of the
First World War
on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the
Royal Flying Corps
(RFC) and the
Royal Naval Air Service
(RNAS).
[4]
Following the
Allied
victory over the
Central Powers
in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time.
[5]
Since its formation, the RAF has taken
a significant role
in
British military history
. In particular, it played a large part in the
Second World War
where it fought its most famous campaign, the
Battle of Britain
.
[6]
The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British
Ministry of Defence
(MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security".
[7]
The RAF describes its mission statement as "... [to provide] an
agile, adaptable and capable
Air Force that, person for person, is second to none, and that makes a decisive air power contribution in support of the UK Defence Mission".
[8]
The mission statement is supported by the RAF's definition of
air power
, which guides its strategy. Air power is defined as "the ability to
project power
from the air and space to influence the behaviour of people or the course of events".
[9]
Today, the Royal Air Force maintains an operational fleet of
various types of aircraft
,
[10]
described by the RAF as being "leading-edge" in terms of technology.
[11]
This largely consists of fixed-wing aircraft, including those in the following roles:
fighter
and
strike
,
airborne early warning and control
,
intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance
(ISTAR),
signals intelligence
(SIGINT), maritime patrol,
air-to-air refuelling
(AAR) and
strategic
&
tactical transport
. The majority of the RAF's rotary-wing aircraft form part of the tri-service
Joint Helicopter Command
in support of ground forces. Most of the RAF's aircraft and personnel are based in the UK, with many others serving on
global operations
(principally
over Iraq and Syria
) or at long-established overseas bases (
Ascension Island
,
Cyprus
,
Gibraltar
, and the
Falkland Islands
). Although the RAF is the principal British air power arm, the
Royal Navy
's
Fleet Air Arm
and the
British Army
's
Army Air Corps
also operate armed aircraft.
History
[
edit
]
Further information:
List of Royal Air Force operations
Main article:
History of the Royal Air Force
Origins
[
edit
]
While the British were not the first to make use of heavier-than-air military aircraft, the RAF is the world's oldest independent air force: that is, the first air force to become independent of army or navy control.
[12]
The RAF was founded on 1 April 1918 (during
World War I
) by the amalgamation of the
Royal Flying Corps
(RFC) and the
Royal Naval Air Service
(RNAS), as recommended in a report prepared by
Jan Smuts
.
[13]
At that time it was the largest air force in the world.
[13]
Its headquarters was located in the former
Hotel Cecil
.
[14]
After the war, the RAF was drastically cut and its inter-war years were relatively quiet. The RAF was put in charge of
British military activity in Iraq
, and carried out minor activities in other parts of the
British Empire
, including establishing bases to protect
Singapore
and Malaya.
[15]
The RAF's naval aviation branch, the
Fleet Air Arm
, was founded in 1924 but handed over to
Admiralty
control on 24 May 1939.
[16]
The RAF adopted the doctrine of
strategic bombing
, which led to the construction of long-range bombers and became its main bombing strategy in the
Second World War
.
[17]
Second World War
[
edit
]
Further information:
Air warfare of World War II
A late-war version of the
Spitfire
, which played a major role in the
Battle of Britain
The Royal Air Force underwent rapid expansion prior to and during the Second World War. Under the
British Commonwealth Air Training Plan
of December 1939, the air forces of
British Commonwealth
countries trained and formed "
Article XV squadrons
" for service with RAF formations. Many individual personnel from these countries, and exiles from
occupied Europe
, also served with RAF squadrons. By the end of the war the
Royal Canadian Air Force
had contributed more than 30 squadrons to serve in RAF formations, similarly, approximately a quarter of
Bomber Command's
personnel were Canadian.
[18]
Additionally, the
Royal Australian Air Force
represented around nine percent of all RAF personnel who served in the European and Mediterranean theatres.
[19]
During the
Battle of Britain
in 1940, the RAF defended the skies over Britain against the numerically superior German
Luftwaffe
. In what is perhaps the most prolonged and complicated air campaign in history, the Battle of Britain contributed significantly to the delay and subsequent indefinite postponement of
Operation Sea Lion
,
Hitler's
plans for an invasion of the UK. In the
House of Commons
on 20 August, prompted by the ongoing efforts of the RAF, Prime Minister
Winston Churchill
made a speech to the nation, where he said "
Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few"
.
[20]
The
Avro Lancaster
heavy bomber was extensively used during the strategic bombing of Germany.
The largest RAF effort during the war was the
strategic bombing
campaign against Germany by Bomber Command. While RAF bombing of Germany began almost immediately upon the outbreak of war at first it was ineffectual; it was only later, particularly under the leadership of
Air Chief Marshal
Harris
, that these attacks became increasingly devastating, from early 1943 onward, as new technology and greater numbers of superior aircraft became available.
[21]
The RAF adopted night-time
area bombing
on German cities such as
Hamburg
and
Dresden
. Night time area bombing constituted the great bulk of the RAF's bombing campaign, mainly due to Harris, but it also developed precision bombing techniques for specific operations, such as the
"Dambusters" raid
by
No. 617 Squadron
,
[22]
or the Amiens prison raid known as
Operation Jericho
.
[23]
Cold War era
[
edit
]
Further information:
Cold War
Main article:
Structure of the Royal Air Force in 1989
Following victory in the Second World War, the RAF underwent significant re-organisation, as technological advances in air warfare saw the arrival of jet fighters and bombers. During the early stages of the Cold War, one of the first major operations undertaken by the RAF was the
Berlin Airlift
, codenamed Operation Plainfire. Between 26 June 1948 and the lifting of the Russian blockade of the city on 12 May 1949, the RAF provided 17% of the total supplies delivered, using
Avro Yorks
,
Douglas Dakotas
flying to
Gatow Airport
and
Short Sunderlands
flying to Lake Havel.
[24]
The
Handley Page Victor
bomber was a
strategic bomber
of the RAF's
V bomber force
used to carry both conventional and
nuclear bombs
.
Before Britain developed its own
nuclear weapons
, the RAF was provided with American nuclear weapons under
Project E
. However, following the development of its own arsenal, the British Government elected on 16 February 1960 to share the country's
nuclear deterrent
between the RAF and submarines of the Royal Navy, first deciding to concentrate solely on the air force's
V bomber
fleet. These were initially armed with nuclear
gravity bombs
, later being equipped with the
Blue Steel missile
. Following the development of the Royal Navy's
Polaris submarines
, the strategic nuclear deterrent passed to the navy's submarines on 30 June 1969.
[25]
With the introduction of Polaris, the RAF's strategic nuclear role was reduced to a tactical one, using
WE.177
gravity bombs. This tactical role was continued by the V bombers into the 1980s and until 1998 by the
Panavia Tornado GR1
.
[26]
[27]
The
Avro Vulcan
was a
strategic bomber
used during the
Cold War
to carry conventional and
nuclear bombs
.
For much of the Cold War the primary role of the RAF was the defence of
Western Europe
against potential attack by the
Soviet Union
, with many
squadrons based in West Germany
. The main RAF bases in RAF(G) were
RAF Brüggen
,
RAF Gutersloh
,
RAF Laarbruch
and
RAF Wildenrath
– the only air defence base in RAF(G). With the decline of the British Empire, global operations were scaled back, and
RAF Far East Air Force
was disbanded on 31 October 1971.
[28]
Despite this, the RAF fought in many battles in the Cold War period. In June 1948 the RAF commenced
Operation Firedog
against Malayan pro-independence fighters during the
Malayan Emergency
.
[29]
Operations continued for the next 12 years until 1960 with aircraft flying out of
RAF Tengah
and
RAF Butterworth
. The RAF played a minor role in the
Korean War
, with
flying boats
taking part.
[30]
From 1953 to 1956 the RAF Avro Lincoln squadrons carried out anti-
Mau Mau
operations in
Kenya
using its base at
RAF Eastleigh
.
[31]
The
Suez Crisis
in 1956 saw a large RAF role, with aircraft operating from
RAF Akrotiri
and
RAF Nicosia
on
Cyprus
and
RAF Luqa
and
RAF Hal Far
on
Malta
as part of
Operation Musketeer
.
[32]
The RAF suffered its most recent loss to an enemy aircraft during the Suez Crisis, when an
English Electric Canberra PR7
was shot down over
Syria
.
[33]
RAF Shackleton flying in formation in 1957 during the
Jebel Akhdar War
in Oman
In 1957, the RAF participated heavily during the
Jebel Akhdar War
in Oman, operating both
de Havilland Venom
and
Avro Shackleton
aircraft. The RAF made 1,635 raids, dropping 1,094 tons and firing 900 rockets at the interior of Oman between July and December 1958, targeting insurgents, mountain top villages and water channels in a war that remained under low profile.
[34]
[35]
The
Konfrontasi
against Indonesia in the early 1960s did see use of RAF aircraft, but due to a combination of deft diplomacy and selective ignoring of certain events by both sides, it never developed into a full-scale war.
[36]
One of the largest actions undertaken by the RAF during the Cold War was the air campaign during the 1982
Falklands War
, in which the RAF operated alongside the
Fleet Air Arm
. During the war, RAF aircraft were deployed in the mid-Atlantic at
RAF Ascension Island
and a detachment from
No. 1 Squadron
was deployed with the Royal Navy, operating from the aircraft carrier
HMS
Hermes
.
[37]
[38]
RAF pilots also flew missions using the Royal Navy's
Sea Harriers
in the air-to-air combat role, in particular
Flight Lieutenant
Dave Morgan the highest scoring pilot of the war.
[39]
Following a British victory, the RAF remained in the
South Atlantic
to provide air defence to the Falkland Islands, with the
McDonnell Douglas Phantom FGR2
based at
RAF Mount Pleasant
which was built in 1984